What is uric acid?
How is it formed?
What are the symptoms of its height?
And how can it be reduced?
Uric acid
It is a chemical that is formed when the body breaks down substances called purines, according to the MedlinePlus database of the National Library of Medicine in the United States.
Purines are normally produced in the body and are also found in some foods and beverages. These foods high in purines include liver, anchovies, mackerel, and dried beans and peas.
Most uric acid dissolves in the blood and is transported to the kidneys;
From there it comes out in the urine, and if your body is making too much uric acid or not removing enough of it, you could get sick.
A high level of uric acid in the blood is called hyperuricemia.
What does high uric acid in the blood mean?
Higher than normal levels of uric acid (hyperuricemia) may be due to:
acidosis
Side effects associated with chemotherapy.
Drought.
Diabetic ketoacidosis.
Excessive exercise.
fructose consumption.
Hyperparathyroidism.
Hypothyroidism.
lactic acidosis
Lead poisoning.
blood cancer.
Medicines such as cyclosporine and diuretics.
Medullary cystic kidney disease.
Obesity.
psoriasis
Purine-rich diet.
Kidney failure.
Eclampsia.
Vitamin B12 deficiency.
What foods contain uric acid?
Foods and drinks that are high in purines increase uric acid levels, including:
Seafood (especially salmon, shrimp, lobsters and sardines), according to the Cleveland Clinic.
red meat.
Organ meats such as liver.
Uric acid and gout
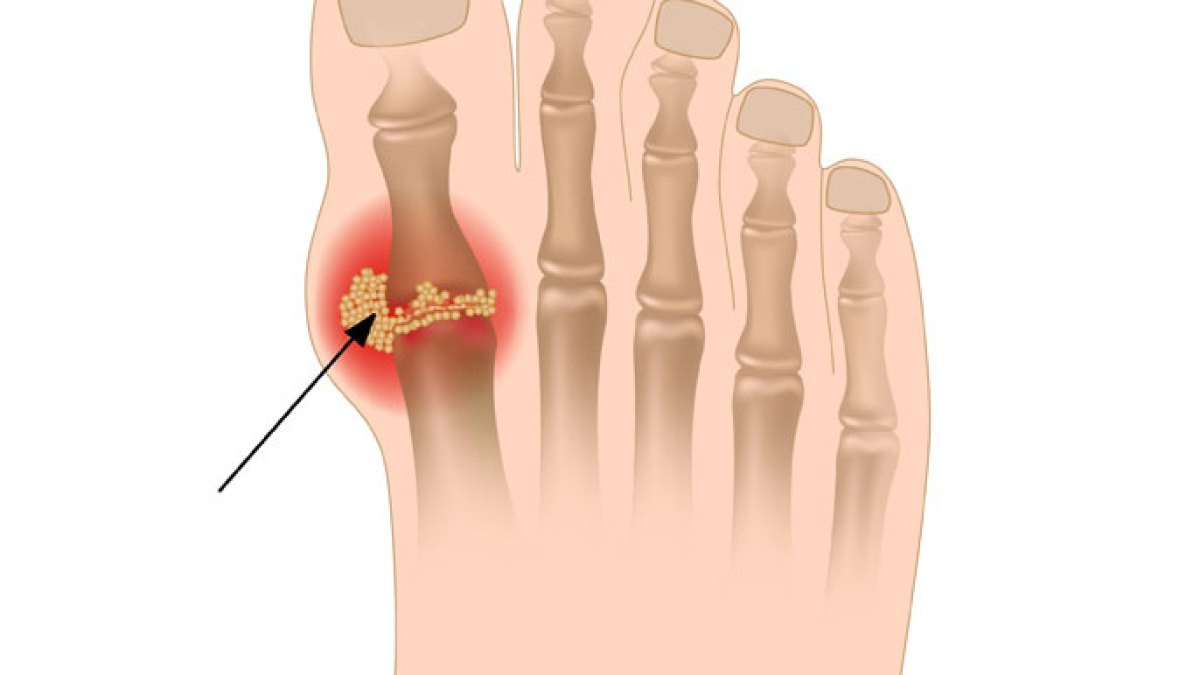
If too much uric acid remains in the body, a condition called “hyperuricemia” occurs. Hyperuricemia can cause crystals of uric acid to form. These crystals can settle in the joints and cause gout, which is a form of arthritis that can It is very painful, and it can also lodge in the kidneys and form kidney stones.
If left untreated, high levels of uric acid can eventually lead to permanent damage to bones, joints, and tissues, and kidney and heart disease.
Research has also shown a link between high uric acid levels and type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and fatty liver disease.
What does high uric acid in the urine mean?
An elevated level of uric acid in the urine may be due to:
Inability of the body to process purines (Lech-Nyhan syndrome).
Some cancers that spread (metastatic cancer).
Rhabdomyolysis, a disease that causes muscle fibers to retract.
Bone marrow disorders.
Fanconi syndrome, which is a disorder of the kidney tubules.
gout.
High purine diet.
Causes of high uric acid
According to MayoClinic, some of the causes of a high level of uric acid in the blood include:
diuretics;
Drinking too much soda or eating too many foods that contain fructose.
Hypertension.
Immunosuppressive drugs.
kidney problems;
blood cancer.
Metabolic syndrome.
Obesity.
Normal uric acid levels in the urine
A 24-hour urine sample is collected. Normal values for uric acid are between 250 and 750 milligrams/24 hours (1.48 to 4.43 mmol/24 hours).
Normal uric acid level in the blood
A blood sample is taken, and normal values are between 3.5 and 7.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
Hyperuricemia can cause crystals to form that settle in the joints and cause gout (Dreams Time)
Low uric acid
Low levels of uric acid may be due to:
Fanconi syndrome.
Hereditary metabolic diseases.
Low purine diet.
Medicines such as atorvastatin, captopril, and enalapril.
Symptoms of high uric acid
Symptoms may not always appear in a person with high or low uric acid levels.
Symptoms may not appear until a person has had levels outside the normal range for a long time, which can cause health problems, according to Medical News Today.
Symptoms of gout that can be caused by high levels of uric acid include:
pain in the joints.
Swelling in the joint.
Warm joints.
Shiny skin around the joints.
Symptoms of kidney stones that can cause high uric acid levels also include:
Back ache.
pain in the side
frequent urination.
urine that is cloudy, has an unusual smell, or contains blood
Nausea or vomiting.
Symptoms of low uric acid
Low uric acid levels are less common than high levels, and a person with low uric acid levels may urinate more than usual, which can cause dehydration if they don't drink enough water.
Treating high uric acid
Certain foods contain purines, which release uric acid when the body breaks them down, and eating a diet too rich in purines can lead to a buildup of uric acid in the blood.
Purines cannot be completely avoided because there are small amounts present in many foods.
However, a person can follow a low-purine diet and take other steps to help lower purine levels.
Foods that contain moderate or high levels of purines include:
Turkey.
Red meat.
oysters.
salmon.
anchovies.
Sardines.
salted fish.
A person with gout may want to limit these foods in their diet.
Anti-inflammatory medications and steroids can reduce pain and inflammation, which can help treat an acute gout attack.
Steps can also be taken to prevent gout attacks, including:
Achieving and maintaining a moderate weight.
Protect your joints with light, low-impact exercises such as walking, cycling and swimming.
A person with gout usually needs a uric acid test every 6 months.
Keeping uric acid levels within a certain range can reduce pain, joint damage, and complications of gout.